算法题-链表相关
链表
链表众多操作可以分解为几个基础操作:反转链表,链表删除,21. 合并两个有序链表 - 力扣(Leetcode)
借用链表考察数据结构:实现LRU 使用双链表+哈希表实现
链表实现整数和:++2. 两数相加 - 力扣(LeetCode)
由基础操作衍生出来的题目:((20230615144645-vetevju ‘重排链表’)) 包括反转与合并
反转链表
使用双指针来进行反转,pre和cur指针
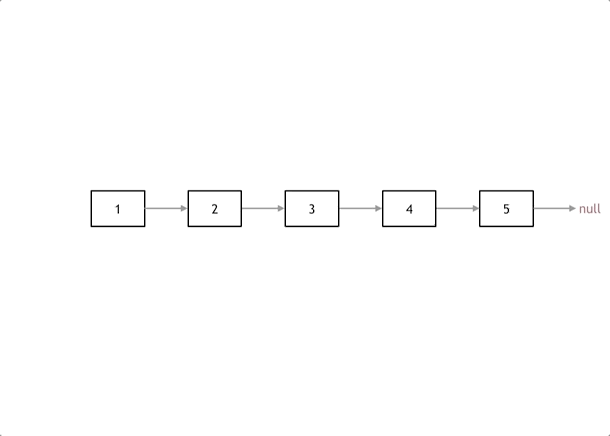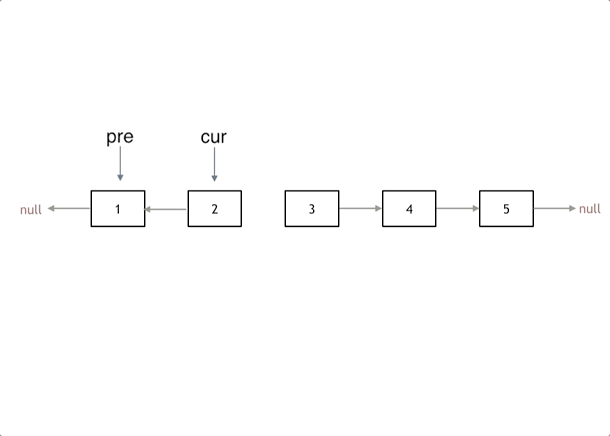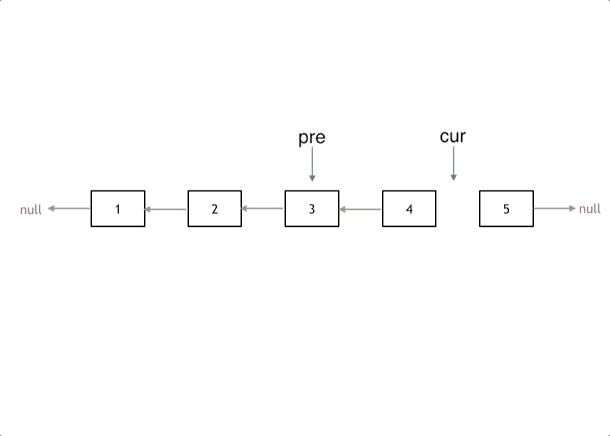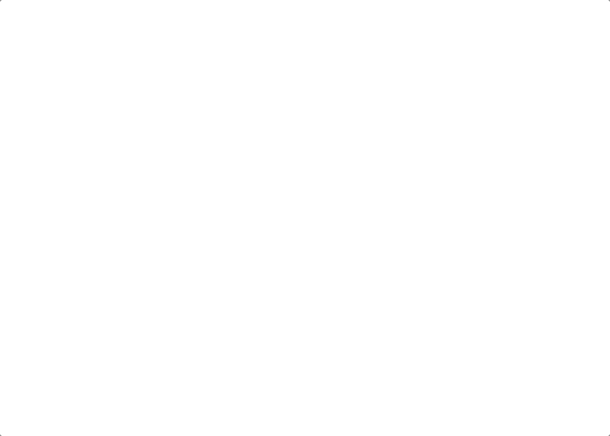
据此可以写出代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| * struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
ListNode* tmp=nullptr;
ListNode* pre=nullptr;
ListNode* cur=head;
while(cur){
tmp=cur->next;
cur->next=pre;
pre=cur;
cur=tmp;
}
return pre;
}
};
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
| ListNode* reverseBetween(ListNode* head, int m, int n) {
ListNode* dummy=new ListNode(0);
dummy->next=head;
ListNode* pre=nullptr;
ListNode* cur=dummy;
for(int i=0;i<m;i++){
pre=cur;
cur=cur->next;
}
ListNode*curPre=nullptr,*tmp=nullptr;
ListNode*after=cur;
for(int i=0;i<n-m+1;i++){
tmp=cur->next;
cur->next=curPre;
curPre=cur;
cur=tmp;
}
pre->next=curPre;
after->next=cur;
return dummy->next;
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| ListNode* reverseKGroup(ListNode* head, int k) {
ListNode* tail=head;
for(int i=0;i<k;i++){
if(tail==nullptr) return head;
tail=tail->next;
}
ListNode* pre=nullptr;
ListNode* cur=head;
while(cur!=tail){
ListNode* tmp=cur->next;
cur->next=pre;
pre=cur;
cur=tmp;
}
head->next=reverseKGroup(tail,k);
return pre;
}
|
链表删除
删除倒数第n个节点 19. 删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点 - 力扣(LeetCode)
注意点:
- 采用虚拟头节点
- 快慢指针,双指针的思想快慢指针移除元素 面试题 02.07. 链表相交 - 力扣(LeetCode) 142. 环形链表 II - 力扣(LeetCode)
给出一个升序排序的链表,删除链表中的所有重复出现的元素,只保留原链表中只出现一次的元素。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
| ListNode* deleteDuplicates(ListNode* head) {
ListNode* cur=head;
ListNode* dummyNode=new ListNode(10001);
dummyNode->next=head;
ListNode* pre=dummyNode;
while(cur&&cur->next){
bool flag=false;
while(cur->val==cur->next->val&&cur->next){
flag=true;
ListNode* tmp=cur->next;
cur->next=cur->next->next;
delete tmp;
}
if(flag) {
pre->next=cur->next;
ListNode* tmp=cur;
cur=pre->next;
delete tmp;
}else{
pre=cur;
cur=cur->next;
}
}
return dummyNode->next;
}
|
链表合并
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
| struct CompareNodes {
bool operator()(const ListNode* a, const ListNode* b) {
return a->val > b->val;
}
};
ListNode* mergeKLists(vector<ListNode*>& lists) {
priority_queue<ListNode*,vector<ListNode*>,CompareNodes> pq;
for(auto list:lists){
if(list)
pq.emplace(list);
}
ListNode* dummy=new ListNode(0);
ListNode* tail=dummy;
while(!pq.empty()){
auto cur=pq.top();
pq.pop();
tail->next=cur;
tail=cur;
if(cur->next){
pq.emplace(cur->next);
}
}
return dummy->next;
}
|
另一种解法,采用递归
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
| public:
ListNode *mergeKLists(vector<ListNode *> &lists) {
if(lists.size() == 0)
return nullptr;
ListNode* head = nullptr;
for(int i = 0; i < lists.size(); ++i){
head = connectList(head, lists[i]);
}
return head;
}
ListNode* connectList(ListNode* p1, ListNode* p2){
if(p1 == nullptr || p2 == nullptr)
return p1 == nullptr ? p2 : p1;
if(p1->val < p2->val){
p1->next = connectList(p1->next, p2);
return p1;
}
else{
p2->next = connectList(p1, p2->next);
return p2;
}
}
};
|
由此方法退出单纯地合并两个链表其实递归就行:
比如合并两个有序递增链表
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| ListNode* Merge(ListNode* pHead1, ListNode* pHead2) {
if(pHead1==nullptr&&pHead2==nullptr) return nullptr;
if(pHead1==nullptr||pHead2==nullptr){
return pHead1==nullptr?pHead2:pHead1;
}
if(pHead1->val<pHead2->val){
pHead1->next=Merge(pHead1->next, pHead2);
return pHead1;
}
else{
pHead2->next=Merge(pHead1,pHead2->next);
return pHead2;
}
return nullptr;
}
|
链表求交
- 有公共节点的时候,N1和N2必会相遇,因为长度一样嘛,速度也一定,必会走到相同的地方的,所以当两者相等的时候,则会第一个公共的节点
- 无公共节点的时候,此时N1和N2则都会走到终点,那么他们此时都是null,所以也算是相等了。
下面看个动态图,可以更形象的表示这个过程~
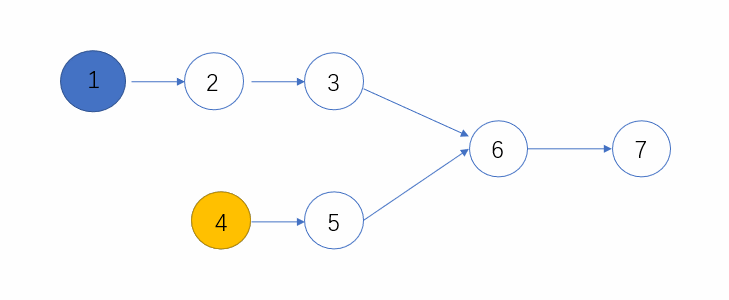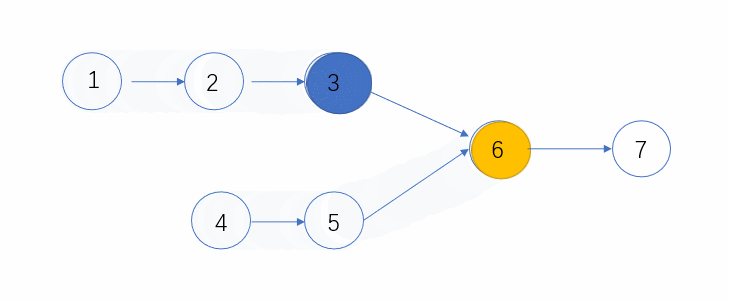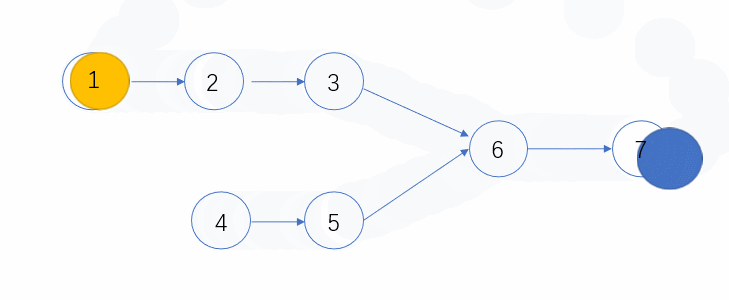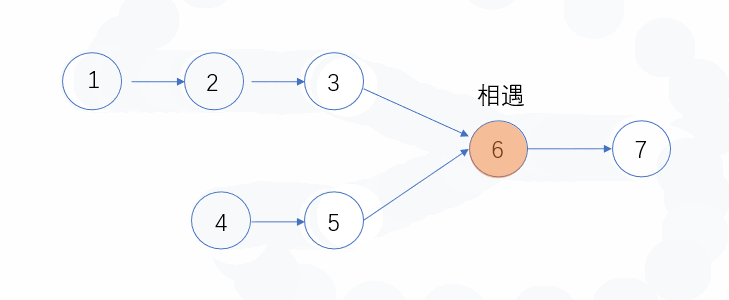
代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| ListNode* FindFirstCommonNode( ListNode* pHead1, ListNode* pHead2) {
ListNode* p1=pHead1,*p2=pHead2;
while(p1!=p2){
p1=(p1==nullptr)?pHead2:p1->next;
p2=(p2==nullptr)?pHead1:p2->next;
}
return p1;
}
|
重排链表
这题卡住的地方在于合并链表处 如何合并到原来的链表里
两个链表l1,l2合并 返回l1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| void mergeList(ListNode* l1,ListNode* l2){
ListNode *tmp1,*tmp2;
while(l1&&l2){
tmp1=l1->next;
tmp2=l2->next;
l1->next=l2;
l1=tmp1;
l2->next=l1;
l2=tmp2;
}
}
|
完整代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
| class Solution {
public:
void reorderList(ListNode* head) {
ListNode* slowIndex=head,*fastIndex=head;
while(fastIndex&&fastIndex->next){
slowIndex=slowIndex->next;
fastIndex=fastIndex->next->next;
}
ListNode* l1=head;
ListNode* l2=slowIndex->next;
slowIndex->next=nullptr;
l2=reverseList(l2);
mergeList(l1, l2);
}
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* root){
ListNode* pre=nullptr,*cur=root;
ListNode* tmp;
while(cur){
tmp=cur->next;
cur->next=pre;
pre=cur;
cur=tmp;
}
return pre;
}
void mergeList(ListNode* l1,ListNode* l2){
ListNode *tmp1,*tmp2;
while(l1&&l2){
tmp1=l1->next;
tmp2=l2->next;
l1->next=l2;
l1=tmp1;
l2->next=l1;
l2=tmp2;
}
}
};
|
题目总结
19. 删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点 - 力扣(LeetCode)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| class Solution {
public:
ListNode* removeNthFromEnd(ListNode* head, int n) {
ListNode* dummpyHead=new ListNode(0);
dummpyHead->next=head;
ListNode *slow=dummpyHead,*fast=dummpyHead;
while(n--&&fast!=nullptr) fast=fast->next;
fast=fast->next;
while(fast!=nullptr){
slow=slow->next;
fast=fast->next;
}
slow->next=slow->next->next;
return dummpyHead->next;
}
};
|
面试题 02.07. 链表相交 - 力扣(LeetCode)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
| class Solution {
public:
ListNode *getIntersectionNode(ListNode *headA, ListNode *headB) {
int lenA=0,lenB=0;
ListNode *curA=headA,*curB=headB;
while(curA){
curA=curA->next;
lenA++;
}
while(curB){
curB=curB->next;
lenB++;
}
int len=abs(lenA-lenB);
if(lenA<lenB) {
swap(headA,headB);
swap(lenA,lenB);
}
curA=headA;
curB=headB;
while(len--) curA=curA->next;
while(curA&&curB){
if(curA==curB) return curA;
curA=curA->next;
curB=curB->next;
}
return NULL;
}
};
|
142. 环形链表 II - 力扣(LeetCode)
思路: 定义快慢指针 fast一次走两步,slow一次走一步 然后相遇就是有环
有环后 从head处和相遇处分别再开始双指针移动 相遇点就是环的入口
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| class Solution {
public:
ListNode *detectCycle(ListNode *head) {
ListNode *slow=head,*fast=head;
bool flag=false;
while(fast&&fast->next){
fast=fast->next->next;
slow=slow->next;
if(fast==slow){
flag=true;
break;
}
}
if(flag==false) return NULL;
ListNode *start1=head;
while(start1!=slow){
start1=start1->next;
slow=slow->next;
}
return slow;
}
};
|
给你两个 非空 的链表,表示两个非负的整数。它们每位数字都是按照 逆序 的方式存储的,并且每个节点只能存储 一位 数字。
请你将两个数相加,并以相同形式返回一个表示和的链表。
你可以假设除了数字 0 之外,这两个数都不会以 0 开头。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
| class Solution {
public:
ListNode* addTwoNumbers(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) {
int left=0;
ListNode* root1=l1;
ListNode* root2=l2;
ListNode* pre=nullptr;
while(root1!=nullptr&&root2!=nullptr){
root1->val+=(root2->val+left);
left=root1->val/10;
root1->val%=10;
pre=root1;
root1=root1->next;
root2=root2->next;
}
if(root2!=nullptr){
pre->next=root2;
root1=pre->next;
}
while(root1!=nullptr&&left!=0){
root1->val+=left;
left=root1->val/10;
root1->val%=10;
pre=root1;
root1=root1->next;
}
if(left>0){
ListNode* node=new ListNode(left);
pre->next=node;
}
return l1;
}
};
|
21. 合并两个有序链表 - 力扣(Leetcode)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
| class Solution {
public:
ListNode* mergeTwoLists(ListNode* list1, ListNode* list2) {
ListNode* dummpyHead=new ListNode(0);
ListNode* root=dummpyHead;
while(list1&&list2){
if(list1->val<list2->val)
{
dummpyHead->next=list1;
list1=list1->next;
}else{
dummpyHead->next=list2;
list2=list2->next;
}
dummpyHead=dummpyHead->next;
}
if(list1){
dummpyHead->next=list1;
}
else if(list2){
dummpyHead->next=list2;
}
return root->next;
}
};
|


