算法题-单调栈相关
单调栈
通常是一维数组,要寻找任一个元素的右边或者左边第一个比自己大或者小的元素的位置,此时我们就要想到可以用单调栈了。时间复杂度为O(n)。
单调栈的本质是空间换时间,因为在遍历的过程中需要用一个栈来记录右边第一个比当前元素高的元素,优点是整个数组只需要遍历一次。
更直白来说,就是用一个栈来记录我们遍历过的元素,因为我们遍历数组的时候,我们不知道之前都遍历了哪些元素,以至于遍历一个元素找不到是不是之前遍历过一个更小的,所以我们需要用一个容器(这里用单调栈)来记录我们遍历过的元素。
在使用单调栈的时候首先要明确如下几点:
- 单调栈里存放的元素是什么?
单调栈里只需要存放元素的下标i就可以了,如果需要使用对应的元素,直接T[i]就可以获取。
- 单调栈里元素是递增呢? 还是递减呢?
注意以下讲解中,顺序的描述为 从栈头到栈底的顺序,因为单纯的说从左到右或者从前到后,不说栈头朝哪个方向的话,大家一定比较懵。
这里我们要使用递增循序(再强调一下是指从栈头到栈底的顺序),因为只有递增的时候,栈里要加入一个元素i的时候,才知道栈顶元素在数组中右面第一个比栈顶元素大的元素是i。
即:如果求一个元素右边第一个更大元素,单调栈就是递增的,如果求一个元素右边第一个更小元素,单调栈就是递减的。
文字描述理解起来有点费劲,接下来我画了一系列的图,来讲解单调栈的工作过程,大家再去思考,本题为什么是递增栈。
使用单调栈主要有三个判断条件。
- 当前遍历的元素T[i]小于栈顶元素T[st.top()]的情况
- 当前遍历的元素T[i]等于栈顶元素T[st.top()]的情况
- 当前遍历的元素T[i]大于栈顶元素T[st.top()]的情况
以题目作为示例:
739. 每日温度 - 力扣(Leetcode)
给定一个整数数组 temperatures ,表示每天的温度,返回一个数组 answer ,其中 answer[i] 是指对于第 i 天,下一个更高温度出现在几天后。如果气温在这之后都不会升高,请在该位置用 0 来代替。
示例 1:
输入: temperatures = [73,74,75,71,69,72,76,73]
输出: [1,1,4,2,1,1,0,0]
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| class Solution {
public:
vector<int> dailyTemperatures(vector<int>& temperatures) {
vector<int> result(temperatures.size(),0);
stack<int> st;
for(int i=0;i<temperatures.size();i++){
if(st.empty()) st.push(i);
else if(temperatures[i]<=temperatures[st.top()]) st.push(i);
else{
while(!st.empty()&&temperatures[i]>temperatures[st.top()]){
result[st.top()]=i-st.top();
st.pop();
}
st.push(i);
}
}
return result;
}
};
|
496. 下一个更大元素 I - 力扣(Leetcode)
nums1 中数字 x 的 下一个更大元素 是指 x 在 nums2 中对应位置 右侧 的 第一个 比 x 大的元素。
给你两个** 没有重复元素** 的数组 nums1 和 nums2 ,下标从 0 开始计数,其中nums1 是 nums2 的子集。
对于每个 0 <= i < nums1.length ,找出满足 nums1[i] == nums2[j] 的下标 j ,并且在 nums2 确定 nums2[j] 的 下一个更大元素 。如果不存在下一个更大元素,那么本次查询的答案是 -1 。
返回一个长度为 nums1.length 的数组ans 作为答案,满足ans[i] 是如上所述的 下一个更大元素 。
示例 1:
输入:nums1 = [4,1,2], nums2 = [1,3,4,2].
输出:[-1,3,-1]
解释:nums1 中每个值的下一个更大元素如下所述:
- 4 ,用加粗斜体标识,nums2 = [1,3,4,2]。不存在下一个更大元素,所以答案是 -1 。
- 1 ,用加粗斜体标识,nums2 = [1,3,4,2]。下一个更大元素是 3 。
- 2 ,用加粗斜体标识,nums2 = [1,3,4,2]。不存在下一个更大元素,所以答案是 -1 。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
| class Solution {
public:
vector<int> nextGreaterElement(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2) {
stack<int> st;
vector<int> res(nums2.size(),-1);
for(int i=0;i<nums2.size();i++){
if(st.empty()) st.push(i);
else if(nums2[i]<=nums2[st.top()]) st.push(i);
else{
while(!st.empty()&&nums2[st.top()]<nums2[i]){
res[st.top()]=nums2[i];
st.pop();
}
st.push(i);
}
}
vector<int>result(nums1.size(),-1);
for(int i=0;i<nums1.size();i++){
int index=0;
while(index<nums2.size()&&nums2[index]!=nums1[i]) index++;
result[i]=res[index];
}
return result;
}
};
|
503. 下一个更大元素 II - 力扣(Leetcode)
给定一个循环数组 nums ( nums[nums.length - 1] 的下一个元素是 nums[0] ),返回 nums 中每个元素的 下一个更大元素 。
数字 x 的 下一个更大的元素 是按数组遍历顺序,这个数字之后的第一个比它更大的数,这意味着你应该循环地搜索它的下一个更大的数。如果不存在,则输出 -1 。
示例 1:
输入: nums = [1,2,1]
输出: [2,-1,2]
解释: 第一个 1 的下一个更大的数是 2;
数字 2 找不到下一个更大的数;
第二个 1 的下一个最大的数需要循环搜索,结果也是 2。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| class Solution {
public:
vector<int> nextGreaterElements(vector<int>& nums) {
stack<int> st;
vector<int> res(nums.size(),-1);
int nums_len=nums.size();
for(int i=0;i<nums.size()*2;i++){
if(st.empty()) st.push(i%nums_len);
else if(nums[i%nums_len]<=nums[st.top()%nums_len]) st.push(i%nums_len);
else{
while(!st.empty()&&nums[i%nums_len]>nums[st.top()%nums_len]){
res[st.top()%nums_len]=nums[i%nums_len];
st.pop();
}
st.push(i%nums_len);
}
}
return res;
}
};
|
42. 接雨水 - 力扣(Leetcode)
给定 n 个非负整数表示每个宽度为 1 的柱子的高度图,计算按此排列的柱子,下雨之后能接多少雨水。
示例 1:

输入:height = [0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1]
输出:6
解释:上面是由数组 [0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1] 表示的高度图,在这种情况下,可以接 6 个单位的雨水(蓝色部分表示雨水)。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
| class Solution {
public:
int trap(vector<int>& height) {
stack<int> st;
int sum=0;
for(int i=0;i<height.size();i++){
if(st.empty()) st.push(i);
else if(height[i]<=height[st.top()]) st.push(i);
else{
while(!st.empty()&&height[i]>height[st.top()]){
int mid=height[st.top()];
st.pop();
if(!st.empty()){
int w=i-st.top()-1;
int h=min(height[st.top()],height[i])-mid;
sum+=w*h;
}
}
st.push(i);
}
}
return sum;
}
};
|
其他解法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| class Solution {
public:
int trap(vector<int>& height) {
if(height.size()<=2) return 0;
vector<int> maxleft(height.size(),0);
vector<int> maxright(height.size(),0);
maxleft[0]=height[0];
maxright[height.size()-1]=height[height.size()-1];
for(int i=1;i<height.size();i++){
maxleft[i]=max(height[i],maxleft[i-1]);
}
for(int i=height.size()-2;i>=0;i--){
maxright[i]=max(height[i],maxright[i+1]);
}
int sum=0;
for(int i=0;i<height.size();i++){
int count=min(maxleft[i],maxright[i])-height[i];
if(count>0) sum+=count;
}
return sum;
}
};
|
84. 柱状图中最大的矩形 - 力扣(Leetcode)
给定 n 个非负整数,用来表示柱状图中各个柱子的高度。每个柱子彼此相邻,且宽度为 1 。
求在该柱状图中,能够勾勒出来的矩形的最大面积。
示例 1:
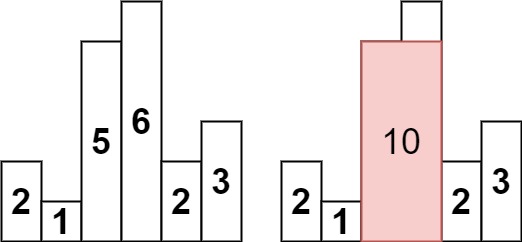
输入:heights = [2,1,5,6,2,3]
输出:10
解释:最大的矩形为图中红色区域,面积为 10
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
| class Solution {
public:
int largestRectangleArea(vector<int>& heights) {
stack<int> st;
heights.insert(heights.begin(),0);
heights.push_back(0);
int res=0;
for(int i=0;i<heights.size();i++){
if(st.empty()) st.push(i);
else{
while(heights[i]<heights[st.top()]){
int mid=st.top();
st.pop();
int w=i-st.top()-1;
int h=heights[mid];
res=max(res,w*h);
}
st.push(i);
}
}
return res;
}
};
|

